Stationary Bike: Video Tutorial & Exercise Guide

Written By: Claude Michael
Updated: Jan 14, 2025
| Workout | Stationary Bike |
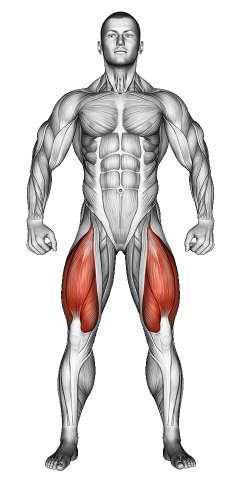
| Primary Muscle Group | Quads |
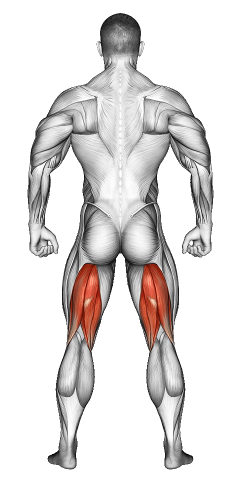
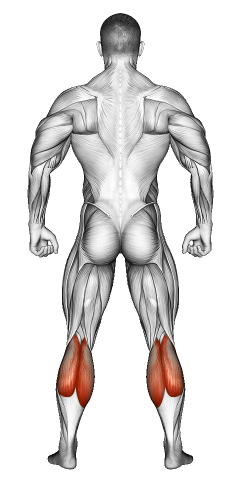
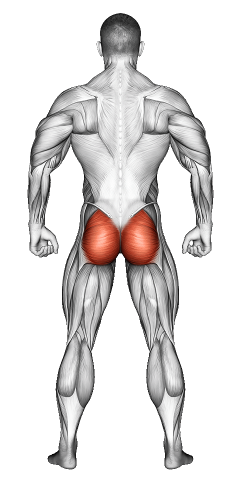
| Secondary Muscle Group | Hamstrings, Calves, , Glutes |
| Equipment Required | Stationary Bike |
| Force Type | Cardio |
| Mechanics | Full-Body Cardio |
| Exercise Type | Endurance and Strength |
| Difficulty | Beginner |
Stationary Bike: Video Tutorial & Exercise Guide
- 1.Stationary Bike: Muscle Groups
- -1.1Primary Muscle Group
- -1.2Secondary Muscle Group
- 2.Stationary Bike: Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.Stationary Bike: Overview
- 4.Stationary Bike: Benefits
- 5.Stationary Bike: Pro Tips & Advanced Techniques
- 6.Stationary Bike: Progression Plan
- 7.Stationary Bike: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Secondary Muscles Group
Stationary Bike: Step-by-Step Guide
- Step 1: Adjust the bike seat to the right height. When you sit, your knees should stay slightly bent when your legs are fully extended on the pedals. Check the handlebars too—they should be at a height where you can hold them comfortably without leaning too far forward.
- Step 2: Sit on the bike and place your feet on the pedals. Strap your feet into the pedal cages or use the clips if your bike has them. Hold the handlebars lightly with both hands, and keep your back straight.
- Step 3: Start pedaling slowly. Focus on smooth, controlled movements to warm up your legs. Keep the resistance light so you can ease into the workout.
- Step 4: Increase your resistance. Turn the resistance knob or adjust the settings on the console to make pedaling harder. Push down with your legs and pull up slightly to create a steady rhythm. Keep your core engaged to stay balanced.
- Step 5: Alternate speeds. Pedal faster for short intervals to increase intensity, then slow down to recover. This helps you build endurance and keeps your workout challenging.
- Step 6: Cool down. Gradually reduce the resistance and slow your pedaling. Keep moving lightly for 2-3 minutes to let your heart rate drop. After you finish, stretch your legs and hips to stay flexible.
Stationary Bike: Overview
The Stationary Bike is a simple, effective way to build leg strength and boost your cardiovascular fitness. It’s low-impact, making it easy on your joints, and perfect for all fitness levels.
Stationary Bike: Benefits
This workout strengthens your legs, glutes, and core while improving your heart health. It’s also great for burning calories and building endurance. You can adjust the resistance to fit your fitness goals, whether you want a light workout or a tougher session.
Stationary Bike: Pro Tips & Advanced Techniques
- Check Your Form: Keep your back straight and your grip on the handlebars relaxed.
- Pedal Smoothly: Avoid jerky movements. Focus on a steady, circular motion.
- Breathe Right: Breathe deeply and steadily to keep your energy up.
- Switch It Up: Mix steady pedaling with intervals of high intensity for a more effective workout.
Stationary Bike: Progression Plan
Beginner
Intermediate
Advanced
Stationary Bike: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What muscles does the Stationary Bike work?
+It targets your legs, glutes, and core while improving cardiovascular endurance.
Is the Stationary Bike good for weight loss?
+Yes! It burns calories and helps you tone your lower body.
How often should I use the Stationary Bike?
+Aim for 2-3 sessions per week and adjust as you get stronger.
What should I avoid during this exercise?
+Don’t hunch your back or grip the handlebars too tightly. Keep your movements controlled and your posture strong.
Is the Stationary Bike good for beginners?
+Absolutely. It’s easy to use and you can adjust the settings to match your fitness level.
Can I do interval training on a Stationary Bike?
+Yes! Alternate between fast pedaling and slow recovery periods for a great cardio workout.
Share
Don’t Wish for It, Work for It – Join the FlexXP Newsletter Today!
Thank you for signing up for the FlexXP Newsletter!
This site is protected and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.